Each year, millions of people step out of poverty by actively embracing modern agricultural techniques, engaging in new market ventures, or seeking new employment. This is good, isn’t it?
However, around the same period, increasing numbers of people are slipping deeper into deprivation owing to health conditions, financial losses and other shocks. Looks sad, huh?
Now, it is expensive to provide marginalized households with financial services, partially because much of their purchases are made in cash. This creates the problem of them being financially excluded.
Do you know how big the problem is?
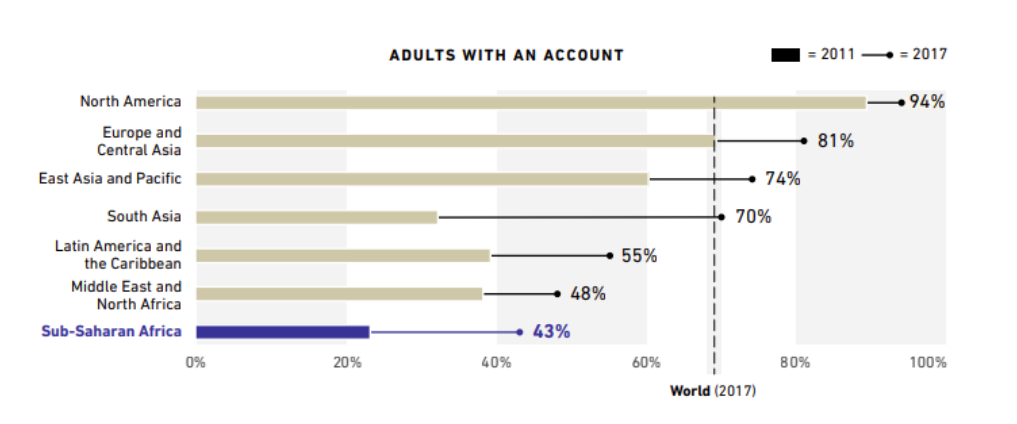
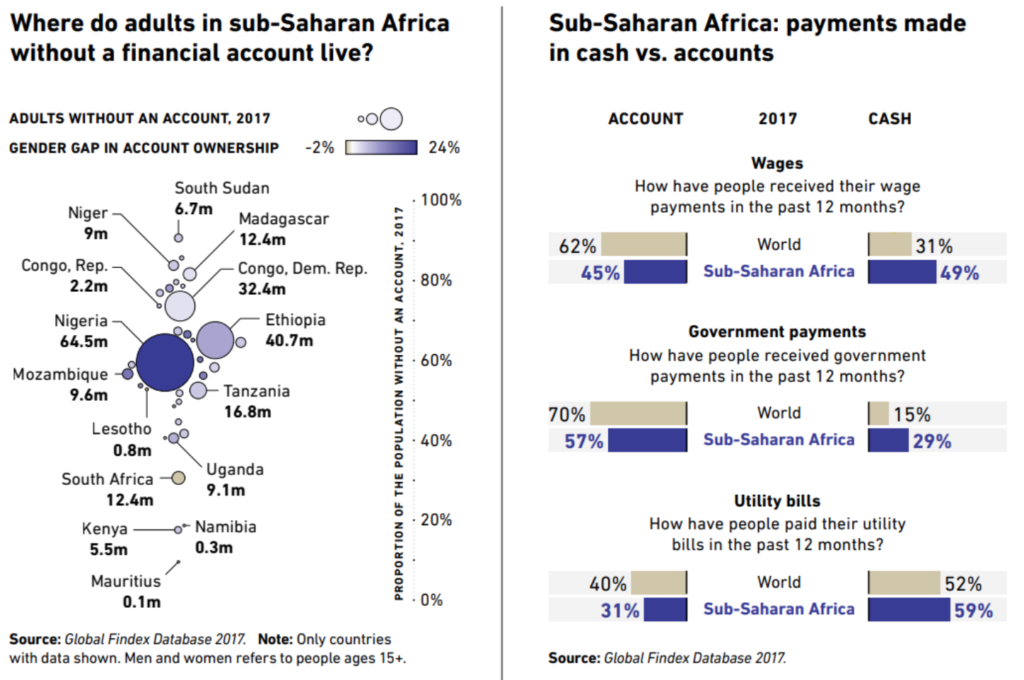
Back in 2017 the problem of living without a bank account (read: financially excluded) accounted for millions of people with huge gender gaps. And though the situation has been improving over the years, Africa is still far away from the world average.
Also, scale of the problem varies: while countries such as Kenya managed to keep the proportion of their financially excluded population around 20%, other regions similar in size (South Sudan) suffer a dramatically worse (90%) exclusion rate.
Yet, the situation can and should be changed.
Financial goods and services have to be made available and affordable to all local and global entrepreneurs, regardless of their specific net worth or scale. But first, achieving financial inclusion means eliminating barriers that prevent people from engaging in and utilizing the finance market to better their lives.
What are those barriers?
– Lack of bargaining power within a household
– Concentration in lower-paying economic activities
– Competing demands on women’s time related to unpaid work
– Lack of assets for collateral
– Lack of formal identifications
– Reduced mobility due to time constraints and social norms
– Lower rates of mobile phone ownership among women
– Lower rates of digital literacy among women
– Inappropriate product offerings
– Lack of gender-specific policies and practicies for product design and marketing
– Inappropriate distribution channels
– Account opening requirements that disadvantage women
– Barriers to obtaining formal identification
– Legal barriers to owning and inheriting property and other collateral
– Lack of gender-inclusive credit reporting systems
– Lack of market and user data for design of targeted policy interventions
Through participants from the government and the public sector, along with business and investment pioneers from the private sector, Nordic countries contribute to poverty reduction and prosperity by creating a platform for a long-term commitment to financial inclusion, assisted by the latest advances in financial technology.
The high rate of possession of smart phones— even among low-income people— creates the potential of serving not just individuals but also agents who can service whole communities with a single device.
Our mission at Aion Sigma is to help governments and private sector partners in a collaborative initiative to deliver financial services to African countries and build more prosperous and safe lives for themselves, their communities and their neighbourhoods. Our team is working to create opportunities of the next phase in financial inclusion and the new technologies and developments in financial goods and services for the unbanked and underserved.
Introduction of digital financial infrastructure is a main factor of cooperation
Dynamics of collaboration make it much more necessary to stay centered on expectations and results
Progress relies on the accomplishment of end goals such as poverty elimination rather than on creating the means to it